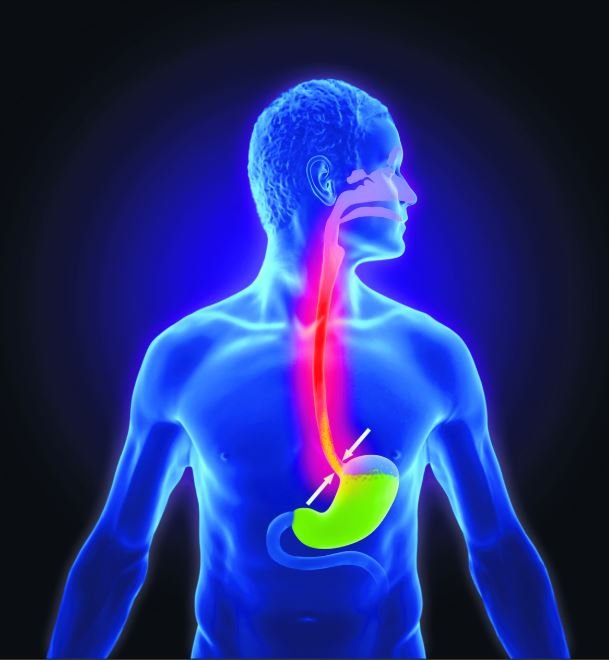
An overview of the risk factors, symptoms, and latest treatment approaches to GORD
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a common disorder of the GI system. A higher incidence occurs in people living in western countries, affecting up to 20 per cent of the population. GORD is defined as “symptoms or complications resulting from the reflux of gastric contents into the oesophagus or beyond, into the oral cavity (including larynx) or lung”. The most common cause is defective functioning of the lower oesophageal sphincter, leading to excessive acid exposure in the lower oesophagus. In healthy people, the ‘angle of His’ where the oesophagus enters the stomach, creates a valve that prevents bile, digestive enzymes, and stomach acid from travelling back into the oesophagus which can cause burning and inflammation of sensitive oesophageal tissue.
Most patients with GORD present with the classic symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation, reporting a burning feeling in the retrosternal area, rising up into the chest and radiating toward the neck, throat, and occasionally the back. It is estimated that between 20 and 40 per cent of patients with heartburn will have a diagnosis of GORD (Patrick, 2011).
Symptoms occur particularly after ingestion of fatty, spicy, citrus products and alcohol. The columnar epithelium lining of the oesophagus cannot withstand acid and this leads to inflammation. Other symptoms include vomiting, halitosis, anorexia, dysphagia, cough and respiratory or oropharyngeal symptoms.
GORD may be just an occasional symptom for some people, but for others it can be a severe, lifelong condition. Left untreated, GORD can cause considerable discomfort and a poor quality-of-life. Medical attention should be sought and symptoms investigated when GORD is severe, occurs several times a week, over-the-counter medications are not helping, dysphagia or symptoms such as vomiting, haematemesis, anaemia or unexplained weight loss occur, that could suggest a more serious problem.
Several factors may increase the risk of developing GORD. First-degree relatives of patients with GORD are four times more likely to develop symptoms, raising the possibility of a strong genetic contribution to the aetiology. Medicines such as calcium-channel blockers, nitrates and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can cause GORD or make the symptoms worse. Risk factors for complications of GORD include advanced age, obesity, alcohol, and tobacco use. There is no clear association between gender and oesophageal stricture, however, men are at greater risk of developing erosive oesophagitis, Barrett’s oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma than women.
The presence of a hiatus hernia increases the likelihood of GORD due to mechanical and motility factors. There is substantial overlap between symptoms of GORD and those of eosinophilic oesophagitis, functional dyspepsia, and gastroparesis, posing a challenge for patient management. Co-existent dysphagia is considered an alarm symptom, requiring investigation and evaluation. GORD may lead to Barrett’s oesophagus, which in turn is a precursor condition for oesophageal cancer. The risk of progression from Barrett’s to dysplasia is estimated at approximately 20 per cent of cases. Oesophageal cancer typically affects people aged between 60 and 80 years, with the most important risk factors being severe long-standing GORD, smoking, and heavy alcohol consumption.
Diagnosis
A presumptive diagnosis of GORD can be made based on the typical symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation. Heartburn is described as a burning, retrosternal, rising sensation associated with meals, although this definition is often poorly understood by the general population. Practitioners need to be aware of this and clarify the nature of the symptoms being discussed when the term ‘heartburn’ is used by patients.
Tests for GORD include, endoscopy, barium swallow or meal, manometry, 24-hour pH monitoring and blood tests. A full blood count (FBC) should be taken to assess for anaemia, which could be a sign of internal bleeding.
GORD can be classified according to the presence or absence of erosions on endoscopic examination. Absence of erosions are classified as non-erosive (NERD), whereas GORD symptoms with erosions is classified as erosive oesophagitis. The primary role of endoscopy is to look for complications and to exclude other diagnoses. Endoscopy is not generally required in the presence of typical GORD symptoms, however, it is recommended for patients who are at higher risk of Barrett’s oesophagus a precursor for developing adenocarcinoma, which is more common in male patients over the age of 50 years.
The risk of progression from Barrett’s to dysplasia is estimated at approximately 20 per cent of cases
Manometry is used to assess how well muscle at the distal end of the oesophagus is functioning. A tube containing pressure sensors can measure the pressures in the oesophagus and help determine whether surgery may be necessary.
A barium swallow, or barium meal, may be required to assess swallowing ability and look for any blockages or abnormalities in the oesophagus.
24-hour pH monitoring may be necessary to measure the acidity level in the oesophagus and confirm a diagnosis of GORD. It is the gold standard and most objective test to diagnose the reflux disease and allows monitoring of GORD patients in their response to medical or surgical treatment.
A urea breath test is the examination of choice for patients under the age of 50 years presenting with dyspepsia. It is recommended as a non-invasive test for active H.pylori infection, but does not confirm or establish a diagnosis of GORD.
One practice for diagnosis is a short-term treatment with proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs), with improvement in symptoms suggesting a positive diagnosis. Short-term treatment with PPIs may help predict abnormal 24-hour pH monitoring results among patients with symptoms suggestive of GORD.
Other causes of chest pain such as heart disease should be ruled out before making the diagnosis. Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) or extra-oesophageal reflux disease is another kind of acid reflux, which causes respiratory and laryngeal symptoms. Unlike GORD, LPR rarely produces heartburn, and is sometimes called ‘silent reflux’.
Treatment and management
The management of GORD includes pharmacotherapy, dietary and lifestyle changes, and in some cases surgery. Initial treatment is guided by the severity of symptoms and treatment is adjusted according to response. The extent of healing depends on disease severity, treatments chosen, and the duration of therapy. Patients should be advised about lifestyle changes, avoidance of excess alcohol and consumption of aggravating foods such as fats. Other measures include smoking cessation and weight reduction if applicable, raising the head of the bed when sleeping, and the avoidance of wearing tight fitting clothing and bending down after a meal.
Initial management for mild symptoms, may include the use of antacids and alginates, which reduce reflux and protect the oesophageal mucosa. Histamine H2 –receptor antagonists, such as ranitidine, may be used to relieve symptoms and permit reduction in antacid consumption. For more severe symptoms and patients with oesophagitis, oesophageal ulceration, oesophagopharyngeal reflux, and Barrett’s oesophagus, treatment involves the use of PPIs. There are a wide range of PPIs available, including omeprazole, pantoprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole and esomeprazole.
Esomeprazole, the S-isomer of omeprazole, has been found to show more improvement than all other PPIs. Current studies have shown that the treatment of reflux oesophagitis with esomeprazole is more cost effective than treatments using any other PPI, providing a greater healing rate at a lower cost. The patient should take their PPI medication first thing in the morning before food. If a morning dose is not sufficient to control symptoms, a second dose in the evening may be required.
If symptoms persist after four-to-six weeks of treatment with a PPI, the patient will need to be reassessed. Non-response to PPIs may suggest an alternative diagnosis, such as peptic ulcer disease, upper gastrointestinal malignancy, functional dyspepsia, eosinophilic oesophagitis or achalasia. When symptoms resolve or abate with PPIs, the treatment can be titrated down to a level which retains remission. This can involve reducing the dose, giving it intermittently or substituting it with a Histamine H2–receptor antagonists. However, for endoscopically confirmed erosive or stricturing disease or Barrett’s oesophagus, treatment with a PPI usually needs to be maintained at the minimum effective dose.
Antacids containing aluminium or magnesium compounds can often relieve symptoms in ulcer dyspepsia and non-erosive GORD. Antacids are best given when symptoms occur or are expected, usually between meals and at bedtime. Conventional doses of liquid magnesium aluminium antacids three-to-four times daily promote ulcer healing but are not as effective as anti-secretory medication. Magnesium containing antacids tend to be laxative in nature, while aluminium-containing antacids can be constipating. Antacid products containing both magnesium and aluminium can reduce these colonic side-effects. Sodium bicarbonate should no longer be prescribed alone for the relief of dyspepsia, but is present as an ingredient in many indigestion remedies. Bismuth-containing antacids are not recommended as absorbed bismuth can be neurotoxic.
Calcium-containing antacids can induce rebound acid secretion and prolonged high doses can cause hypercalcemia and alkalosis. Simeticone, added to an antacid, is an anti-foaming agent to relieve flatulence and can be useful for the relief of hiccups in palliative care. Antacids should not be taken at the same time as other medication, as they may impair absorption and damage the enteric coating of other medication.
Caution must always be maintained with the use of H-2 receptor antagonists and PPIs as they can mask the symptoms of gastric cancer. Particular care is required in patients presenting with alarming features. In such cases, malignancy should be ruled out before treatment commences. Side-effects of H-2 receptor antagonists include diarrhoea, headache, and dizziness and the H-2 receptor antagonist cimetidine should be avoided in patients stabilised on warfarin, phenytoin and theophylline. Side-effects of PPIs include GI disturbances, dizziness, headache and sleep disturbances. Patients at risk of osteoporosis on PPIs should maintain an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D and if necessary receive other preventative therapy. Long-term use of PPIs has been linked to complications, such as vitamin and mineral malabsorption, pernicious anaemia, gastrointestinal infections, gastric cancer, and dementia.
It is estimated that between 20 and 40 per cent of patients with heartburn will have a diagnosis of GORD. Symptoms occur particularly after ingestion of fatty, spicy, citrus products and alcohol.
Pregnant women
If GORD is unresponsive to diet and lifestyle changes in pregnant women, antacids or alginates can be used. If this is ineffective ranitidine a H2–receptor antagonists may be used. The PPI omeprazole is reserved for pregnant women with severe or complicated reflux disease.
Children and infants
GORD is common in infancy but most symptoms resolve without treatment between 12 and 18 months. Mild to moderate reflux without complications in infants can usually be managed by changing the frequency and volume of feed, or a thickened formula feed can be used if advised by a dietician. If necessary, suitable alginate preparations can be used instead of thickened feeds. For older children lifestyle changes may be helpful, followed if necessary by an alginate-containing preparation. Infants or children who do not respond to these measures or who have complications such as oesophagitis or a respiratory disorder, need to be referred to a hospital specialist as a H2–receptor antagonists may be required to reduce acid secretion. Omeprazole may be required if the oesophagitis is resistant to the H2–receptor blockade.
Surgical treatment
Surgery for severe GORD, recommended only for those who do not improve with PPIs, includes Nissen fundoplication, LINX, magnetic sphincter augmentation and transoral incisionless fundoplication. The Nissen fundoplication procedure involves the upper part of the stomach being wrapped around the lower oesophageal sphincter to strengthen the sphincter, prevent acid reflux and to repair a hiatal hernia. Uncertainty surrounds the benefits of surgery versus long-term medical management with PPIs and GORD patients with no response to PPIs are less likely to do better after surgery.
In summary
GORD is a common disorder, and is one of the most frequent conditions encountered in primary care. Treatment and management of GORD symptoms is important and early intervention has the potential to reduce serious complications. The goal of treatment is to effectively control symptoms, prevent complications and improve the patient’s quality of life. Special attention should focus on reducing the rate of refractory GORD and complications such as Barrett’s oesophagus and adenocarcinoma.
Knowledge and understanding of the safe and effective use of medications in the treatment of GORD especially PPIs, prevents inappropriate use, and addresses their adverse reactions and interactions with other medications. The clinical benefits and risk of using PPIs should be evaluated for each individual. Assessment, monitoring, audit and evaluation for disease activity, progression, and effects of the therapeutic regime on a patient with GORD is important and a continuous process. For patients requiring long-term PPI therapy the clinical effects should be reviewed regularly and treatment adjusted as required. The lowest dose of a PPI that controls symptoms should be used. Implementing person-centred care, monitoring and evaluating symptoms, outcomes and responses to therapy plays a pivotal role in managing the illness and improving the patient’s quality of life.







Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.